Performance
![]() Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs) packets to transfer the process images. All process data communication is handled by the slave controller hardware. Combined with these features, this makes EtherCAT
Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs) packets to transfer the process images. All process data communication is handled by the slave controller hardware. Combined with these features, this makes EtherCAT![]() ***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs a high-performance distributed I/O system: Process data exchange with 1000 distributed digital I/O takes about 30 µs, which is typical for a transfer of 125 byte over 100Mb/s Ethernet. Data for and from 100 servo axes can be updated with up to 10 kHz. Typical network update rates are 1-30 kHz, but EtherCAT can be used with slower cycle times, too, if the DMA
***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs a high-performance distributed I/O system: Process data exchange with 1000 distributed digital I/O takes about 30 µs, which is typical for a transfer of 125 byte over 100Mb/s Ethernet. Data for and from 100 servo axes can be updated with up to 10 kHz. Typical network update rates are 1-30 kHz, but EtherCAT can be used with slower cycle times, too, if the DMA![]() "Dynamic memory allocation"
DMA is the allocation of memory storage for use in a computer program during the runtime of that program. It can be seen also as a way of distributing ownership of limited memory resources among many pieces of data and code load is too high on your PC.
"Dynamic memory allocation"
DMA is the allocation of memory storage for use in a computer program during the runtime of that program. It can be seen also as a way of distributing ownership of limited memory resources among many pieces of data and code load is too high on your PC.
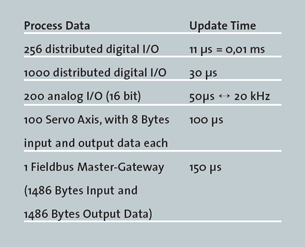
Table 5-4: EtherCAT Performance Overview
The communication with 100 servo axes is also extremely fast: every 100µs, all axes are provided with command values and control data and report their actual position and status. The Distributed Clocks technique enables the axes to be synchronized with a deviation of significantly less than 1 microsecond. And even at this pace, there is more than sufficient bandwidth![]() In computer networking, bandwidth often refers to a data rate measured in bits/s, for example, network throughput. The reason for the connection of data rate with the term bandwidth is that the limit to the data rate of a physical communication link is related to its bandwidth in hertz for asynchronous communications such as TCP/IP, parameter download or diagnostic data upload.
In computer networking, bandwidth often refers to a data rate measured in bits/s, for example, network throughput. The reason for the connection of data rate with the term bandwidth is that the limit to the data rate of a physical communication link is related to its bandwidth in hertz for asynchronous communications such as TCP/IP, parameter download or diagnostic data upload.






